





5. Secondary Cache Interface

5.4 Secondary Cache Way Prediction Table
The primary and secondary caches are two-way set associative. However, the implementation of the secondary cache is different than the primary caches.
The primary caches read simultaneously from two separate tag arrays, corresponding to each way in the cache, and then select the data based on the result of two parallel tag compares.
The secondary cache does not use this implementation because it would either require too many pins to read in two full copies of the data and tags, or add latency to externally multiplex two banks of memory. Instead, a way prediction table is used to determine which way to read from first.
The way prediction table is internal to the processor and has 8K one-bit entries, each entry corresponding to a pair of secondary cache blocks. The bit entry indicates which way of the addressed set has been most-recently used (MRU). When the secondary cache is accessed, this prediction bit is used as an address bit; thus the two ways in the secondary cache are shared in the same SSRAM bank.
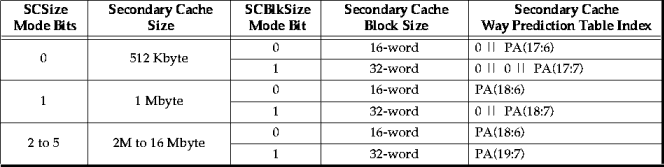
The secondary cache way prediction table is indexed with a subset of 11 to 13 bits of the physical address, based on both the secondary cache block size, and the secondary cache size, as shown in Table 5-3. "0 ||" indicates a zero bit concatenated to the address to pad the index out to a full 13-bits.
Table 5-3 Secondary Cache Way Prediction Table Index
Three states are possible in the way prediction table:
- the desired data is in the predicted way
- the desired data is in the non-predicted way
- the desired data is not in the secondary cache
The tags for both ways are read "underneath" the data access cycles in order to discern as rapidly as possible which of these states are valid. This reading is possible because it takes two accesses to read a primary data block (8 words) and 4 cycles to read a primary instruction block (16 words); thus the bandwidth needed to read the tag array twice exists in all cases. Only an extra address pin to the tag array is needed to make this operation parallel and this is implemented by the SCTWay pin.
The three possible states are handled in the following manner:
- If, after reading the tags for both ways, it is discovered that the data exists in the predicted way, the processor continues normally.
- If the data exists in the non-predicted way, the processor accesses this non-predicted way in the secondary cache and updates the way prediction table to point to this way.

The way prediction table can cover up to a 2 Mbyte secondary cache when the secondary cache block size is 32 words. If the secondary cache exceeds this size, the accuracy of the way prediction table diminishes slightly. However, the extremely large performance gain made by making the secondary cache larger far outstrips any performance loss in the way prediction table.






Copyright 1995, MIPS Technologies, Inc. -- 29 JAN 96



Generated with CERN WebMaker








![]()









